Pet Vaccinations: Complete Guide for New Pet Owners
The process of getting a new pet at home is full of happiness, cuddles, and enchantment. However, with love and games, there is the need to take care of your little pet to make sure that it is healthy and safe. Vaccination of your pet is one of the most significant actions towards providing a long and happy life to them.
Vaccines of pets save dogs and cats against harmful illnesses which otherwise can be fatal. Like human beings, pets should have vaccinations at the right time to develop resistance and protect themselves against common infections. Those who are new pet owners might be overwhelmed by the information about what vaccines are required, when to be received, and how much it will cost but, with the help of this guide, it will turn out to be a non-complicated task to undertake.
We are going to take you through all you should know about pet vaccinations, including vaccination types and schedules, cost, side effects and frequently asked questions so that you can provide your furry friend with a healthy start they need.
What are Pet Vaccinations?
Pets are exposed to various diseases that are transmitted fast and lead to serious health complications just like human beings. Vaccinations are medical preparations, which are designed to prevent these diseases in pets. They do so by making the immune system of your pet identify and eliminate deadly viruses or bacteria before it can result in an infection.
In layman terms, a vaccine is a sort of a drill to the body of your pet. When they have been vaccinated, their immune system is enhanced and it is ready to protect against any further exposure to the same disease. This is not only useful in maintaining the health of your pet but also in cutting the chances of infecting other animals in your locality.
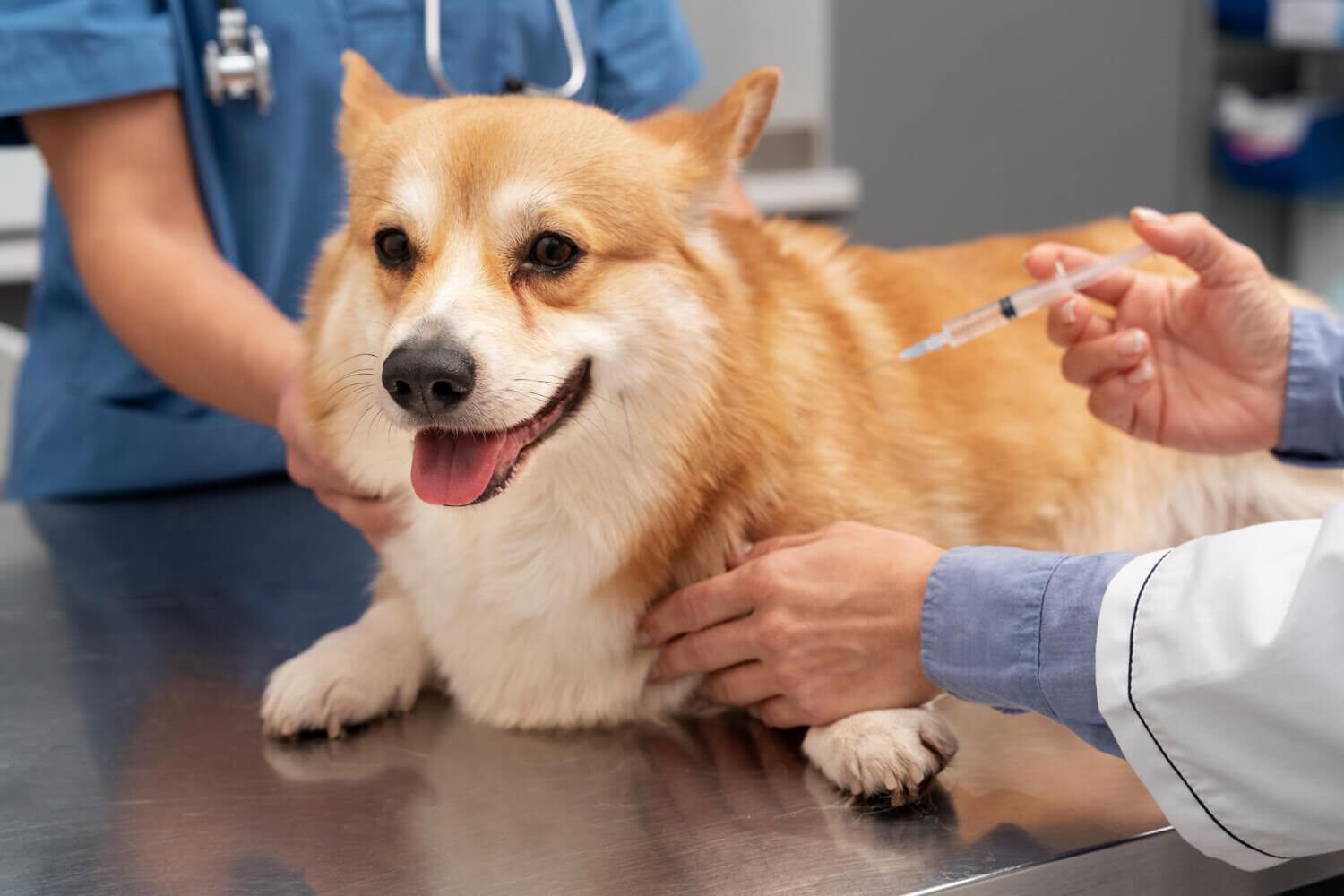
Injections are the most common method of providing a vaccination, and vets adhere to a specific schedule to make sure that the animal receives maximum protection during the appropriate age and at the appropriate stage of life.
Why Are Pet Vaccinations Important?
Vaccinations are not just a normal check-up medical procedure, but it is the safeguard of the health of your pet. A large number of diseases that impact dogs and cats can spread very fast, have long-term health complications, or even result in the death of the animal. Vaccination provides you with a fighting chance to prevent these threats in your pet and in most cases avoids sickness.
New pet owners can also be at peace because of vaccinations. You can be sure that your furry friend is safe when you play outside or see other animals, visit grooming salons and pet shows. The pets that are vaccinated do not pass the diseases as well hence maintaining the larger community of pets healthy.
Actually, numerous boarding facilities, grooming salons and pet friendly events demand to see evidence of vaccination before they are permitted in. Hence, it is not only regarding the health of your pet; taking them to the veterinary clinic regularly is the way to make sure they can lead a richer life with more friends.
Types of Pet Vaccinations
Vaccinations of pets are categorized widely into groups depending on their necessity with regard to the health of a pet. There are vaccines that are a prerequisite in all dogs and cats, whereas others are based on their way of life, surroundings and their risks of exposure.
The knowledge of these types will guide you and your vet to develop the appropriate vaccination plan of your furry friend.
Primary Types of Pet Vaccinations:
Core Vaccines – these are the important vaccines that all pets should get since they are protecting against very serious and widespread diseases.
Non-Core Vaccines – These are optional vaccines that are prescribed due to lifestyle, travel history, or exposure to specific risk factors.
Booster Shots – Booster doses are administered after initial vaccine in order to sustain immunity.
Annual/Periodic Vaccines – Vaccines that are supposed to be repeated at regular intervals, typically once a year or on the recommendation of your vet.
Vaccinations Every Dog Needs
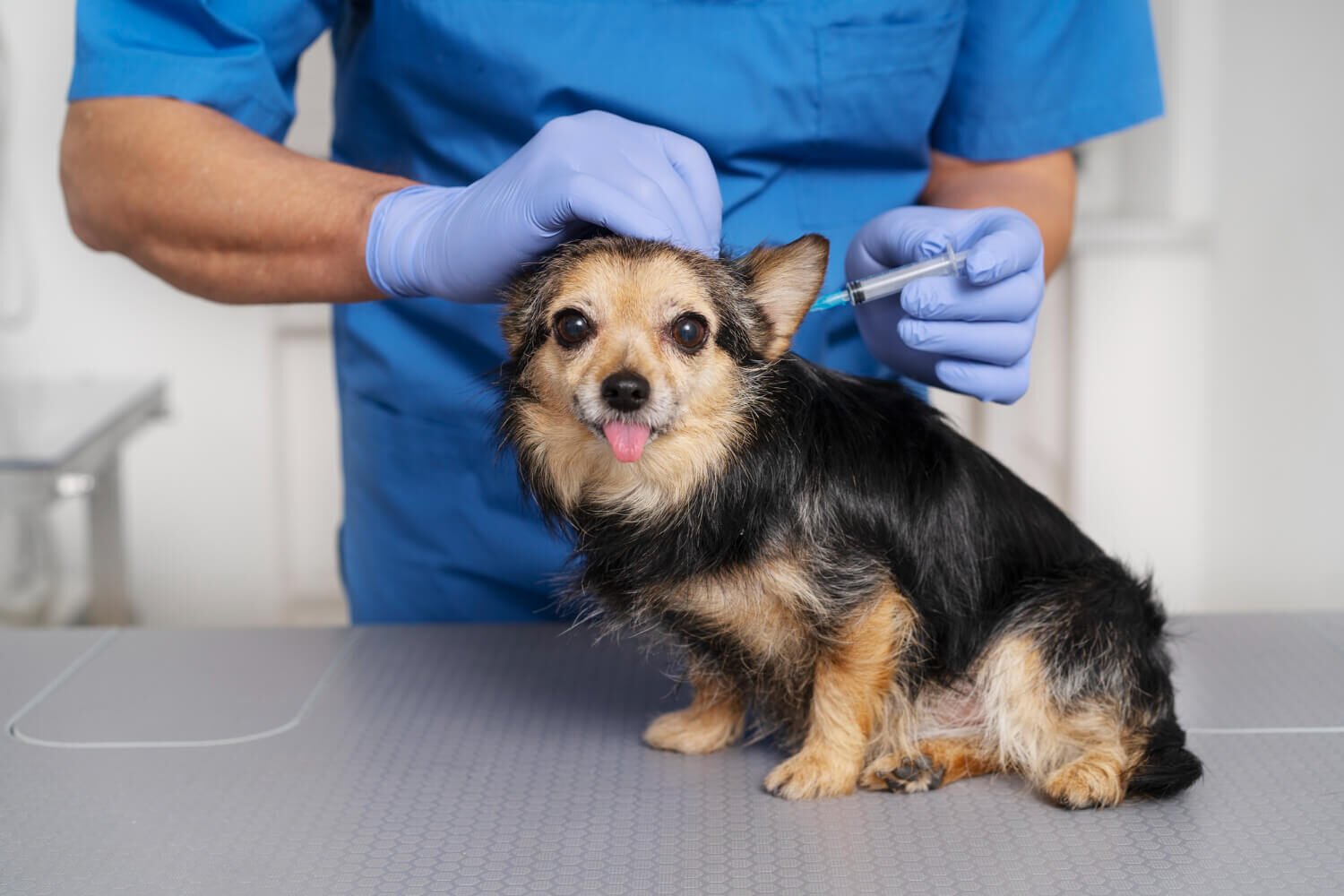
Dogs are social, active and curious in nature, and these characteristics also make them susceptible to a significant number of diseases. This is why some inoculations are mandatory to each and every dog irrespective of the type and the place of residence. Such immunization shields them against very contagious and even life threatening diseases.
There are some that are mandatory by law (such as rabies), and others that are highly encouraged as they are necessary so that your dog can be safe when mingling with other pets, outdoor play, or even a trip to the vet or the groomer.
Core Vaccinations for Dogs:
Rabies Vaccine – It is also legal; it prevents the rabies virus that is lethal.
Canine Distemper Vaccine – It prevents an infectious virus, which attacks the respiratory, digestive and nervous systems.
Canine Parvovirus Vaccine – These are important in the prevention of a severe and in most cases fatal gastro intestinal infection.
Canine Adenovirus (Hepatitis) Vaccine – Protects liver infections caused by adenovirus.
Non-Core Vaccines (Lifestyle-Risk):
Leptospirosis Vaccine – Recommended in dogs that are in the rural areas or have contact with the water bodies.
Kennel Cough (Bordetella) Vaccine – Recommended in dogs that are frequently social and those that are frequently kept in boarding houses.
Lyme Disease Vaccine – As should be given when your dog is living or travelling in an area that contains ticks.
Canine Influenza Vaccine – To provide extra coverage in areas of reported outbreaks.
Related Blog: Dog Vaccinations: Essential Shots Every Dog Needs
Vaccinations Every Cat Needs
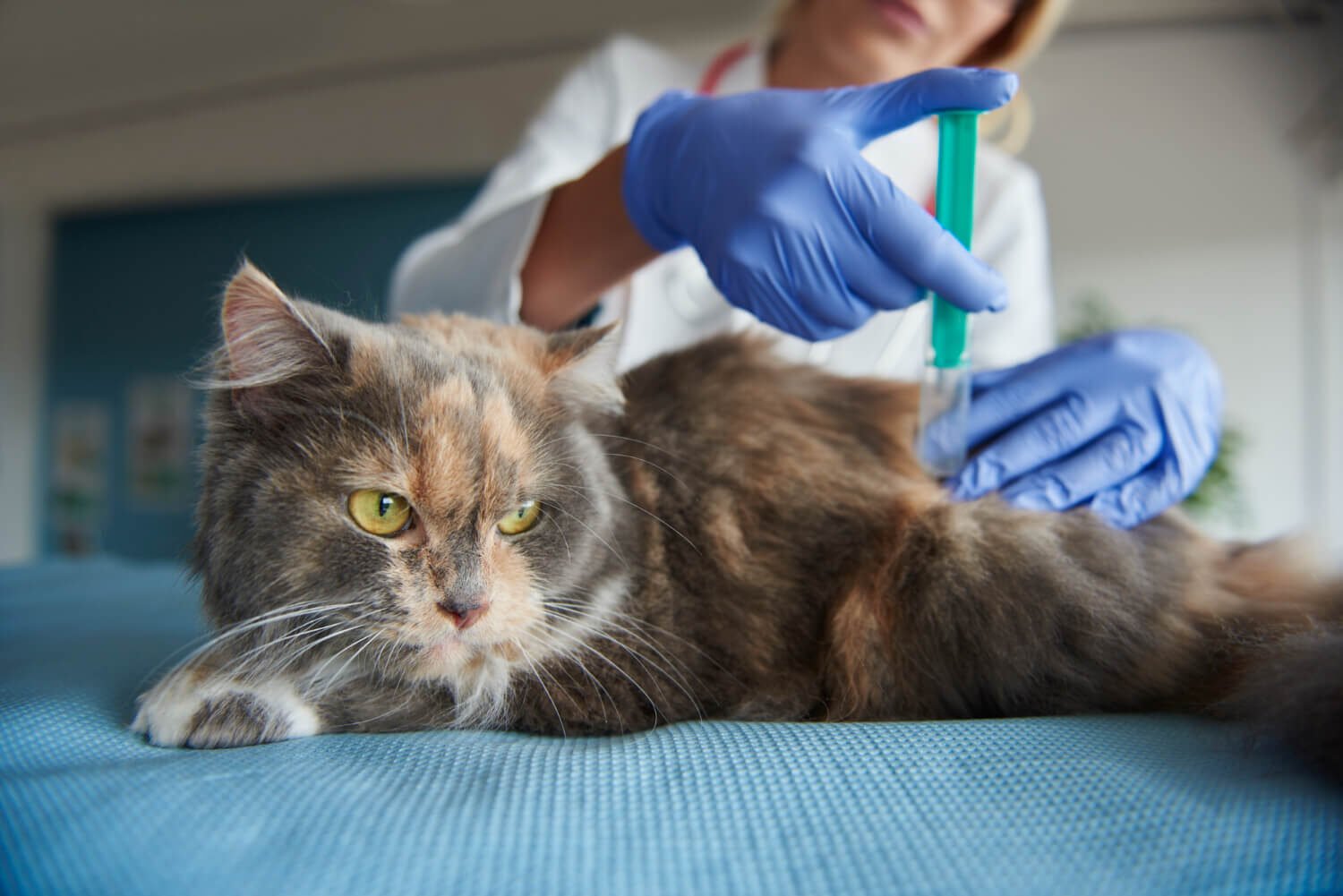
Cats can seem self-sufficient, and no-maintenance, nevertheless, their health requires the timely vaccination, too, to be effective. Some viruses can be spread through the air, clothes, or other pets therefore even indoor cats can contract some of these diseases. Not only are vaccines protecting your cat but also the other cats are not contracting the infectious diseases in the feline population at large.
Like dogs, cat vaccination can be subdivided into core (vaccination needed by every cat) and non-core (vaccination is needed based on the lifestyle and environment). Your vet will help you to make the right decision of the type, which is the most appropriate one in relation to your furry friend.
Core Vaccinations for Cats:
Rabies Vaccine – Inoculation against the deadly rabies virus; it may be legally mandatory.
Feline Panleukopenia (Distemper) Vaccine – Aids in cancer prevention against a highly transmittable and lethal virus infection.
Vaccine Feline Herpesvirus (FHV-1) – Vaccine prevents the respiratory infections that can cause sneezing, fever and eye complications.
Feline Calicivirus (FCV) AB – Protects against another popular cause of respiratory illness and oral well-being.
Non-Core Vaccinations (Lifestyle and Risk-Based):
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) Vaccine – Recommended that they are applied to outdoor cats or in the homes that have more than one cat.
Bordetella Vaccine – useful to cats that tend to spend their time in shelters, boarding houses, or grooming salons.
Chlamydophila felis Vaccine – This is a bacteria that has been known to be the cause of eye and respiratory infections, thus the protection it provides.
Related Blog: Cat Vaccinations: Protecting Your Feline Friend from Diseases
Cost of Pet Vaccinations in India
Vaccinations are a significant expenditure in pet care to new pet owners. The positive aspect is that in India it is affordable to have vaccination relative to the cost of treating serious diseases in the long run. It is possible that the actual price may change as per the city, veterinary hospital, and the kind of vaccination (Indian or imported), but having an approximation will give a head-start.
Usually, core vaccines are cheaper and more accessible, whereas non-core and imported vaccines might be slightly more expensive. A majority of the vets also provide year-long vaccination packages, which are simpler and cheaper to pet parents.
The annual average cost of full vaccination of a dog or a cat in India may range between 2000 to 6000 rupees, based on the breed of an animal, its age, and additional health needs. You should go to your local vet to have the real breakdown.
Approximate Cost Range:
Basic vaccines (Dogs and Cats): 500-1200 per dose.
Non-core vaccines: ₹800 – ₹1,500 per dose.
Rabies vaccine: ₹300 – ₹500 per dose.
Vaccination packs (vet clinics/pet hospitals): ₹2,500 -6,000 per year.
Risks and Side Effects of Vaccinations
Despite the fact that the practice of pet vaccination is neither widely dangerous nor highly effective, it is quite natural that pet owners care about the possible side effects. The reaction of pets in most occasions to vaccines is positive and the reaction they develop is not very severe and does not last long. Serious side effects are extremely infrequent and possessing the awareness of them will help you do things quickly in case it is necessary.
A veterinarian will never inject a vaccine before ensuring that it is safe to your pet which is based on the age, breed and health condition. You should never fail to closely monitor your pet in the few hours following a vaccine so as to check whether it is comfortable.
Common Side Effects (Temporary and Mild):
- Minor swelling or tenderness in the area of injection.
- Mild fever or fatigue
- Loss of appetite (increased), 1-2 days.
- Sneezing or coughing (especially following nasal inoculations)
Frequent and more Severe Side Effects (Vet attention necessary):
- Constant diarrhea or vomiting.
- Protrusion of face or limbs.
- Difficulty with breathing (most likely an allergic reaction)
- Continuous high fever
- Fainting or epileptic attack (extremely rare)
FAQs About Pet Vaccinations
The schedules and effectiveness of vaccination as well as their safety are commonly subject to doubts among pet parents. The following are some of the most frequently asked questions that are answered effectively:
Q1. What happens if I miss a booster shot?
Lack of a booster can weaken the immunity of your pet against some illnesses. In case of forgetfulness, there is no need to panic because you can just consult your vet who might resume the schedule or administer a catch up dose so that your pet is not at risk.
Q2. Do pets really need vaccines every year?
There are those that have a life time immunity with some vaccines and others that need annual boosters. Depending on the age, lifestyle of pets, and diseases in the area, your vet will prescribe the appropriate schedule. Consistent examinations can keep your pet on time.
Q3. At what age should pets start vaccinations?
At 6-8 weeks of age, puppies and kittens normally begin to be vaccinated. A set of injections is administered to them after a gap of some weeks so as to develop high resistance. Also, adult pets that are not vaccinated must be vaccinated as quickly as possible.
Q4. Can vaccines be given at home?
It’s not recommended. A veterinarian should ensure that vaccinations are stored, manipulated as well as administered appropriately. Your pet can also be examined by a vet and then vaccinated as this will minimize any risks of side effects.
Q5. Are imported vaccines better?
The fact that imported vaccines may be thought of as more advanced does not imply that the Indian-manufactured vaccines are ineffective and unsafe. Selection will be based on availability, price and the recommendation of your vet.
Conclusion
Vaccinations are one of the best investments one can make on the health of their pet. They prevent life threatening illnesses and reduce the likelihood of infections and also give your pet an opportunity to live a long and happy life.
As a new pet parent it may be difficult to establish a proper vaccination schedule at the start but with a veterinarian by your side it can be a regular thing. Never forget- never forget–it is always better (and cheaper) to prevent than cure. By keeping the dogs up to date on their vaccinations you are not only protecting your pet but also making your community of pets healthier.